發現荷爾蒙的作用機制
薩塞蘭(Earl W. Sutherland, Jr)

Earl W.
Sutherland, Jr (1915-1974)
The
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, 1971
1971年諾貝爾生理醫學獎頒發給發現荷爾蒙作用機制(Studies
on the Mechanism of Hormone Action)的薩塞蘭(Earl W. Sutherland, Jr)。(1,4,5)
薩塞蘭(Earl W. Sutherland,
Jr)生於公元1915年11月19日的美國堪薩斯州,卒於1974年,享年60歲。1942年曾在Barnes Hospital擔任實習醫師。1940~1953年間於School
of Medicine, Washington University先後擔任藥理學助教、講師及生物化學的講師、副教授,之後於1953~1963年間在School
of Medicine, Western Reserve University擔任藥理學教授及系主任。1963年後,轉任Vanderbilt
University, School of Medicine的生理學教授。1967年時,他成為American Heart Association的職業研究員。薩塞蘭參加過許多與醫學、生理學及生物化學相關的學會,畢生致力於學術研究,在從事研究工作前,是個喜歡親近病患的醫生。(2)
1953年,薩塞蘭醫生自歐陸戰場回國,來到美國聖路易市華盛頓大學的生物化學系(School
of Medicine, Washington University)。當時薩塞蘭受到Carl Ferdinand Cori教授(1947年諾貝爾生理醫學獎得主之一)的激勵,開始從事研究。選定的研究題目是:激素(hormone,在此特指腎上腺素)透過什麼樣的機制來活化肝醣分解脢(phosphorylase),以加速細胞內肝醣(glycogen)分解成葡萄糖(glucose),作為供應能量的來源。(3)
薩塞蘭首先發現當肝臟組織受到腎上腺素(epinephrine)刺激的時候,細胞內的肝醣分解脢會被活化,當它被活化的時候,酵素會接上許多磷酸;而活化的肝醣分解脢接上的磷酸若經由去磷酸脢(phosphatase)的作用去除之後,就會失去活性。這是第一個例子證明:細胞裡的酵素可藉由磷酸化與否,來調控酵素的活性。(3)
薩塞蘭接著發現,其實激素本身不會進入細胞,所以也不能直接控制細胞內部各種酵素的活性,於是他懷疑有其他的物質在細胞內作內應,使激素的訊息得以傳遞到細胞內。他發現激素主要是先作用在細胞膜上,然後細胞膜內側就會釋放出一些小分子到細胞內部,事實上正是由這些小分子在調控細胞內種種酵素的活性,以完成細胞激素的反應。於是,他把激素視為體內負責細胞間通訊的「一級訊號」(primary messenger),而把激素刺激細胞膜後,在細胞內產生的調控分子稱為「二級訊號」(secondary
messenger)。(3)
他並且證實了體內許多不同的激素,都是利用cyclic AMP作為二級訊號。故腎上腺素(primary messenger)會引發細胞內產生cyclic AMP(secondary
messenger),而cAMP會對細胞內許多酵素行磷酸化作用(phosphorylation)使之轉變為具有活性的酵素。接著他又進一步發現激素實際作用的部位為adenyl
cyclase,能使cytosolic ATP轉變為cAMP。(3,6)
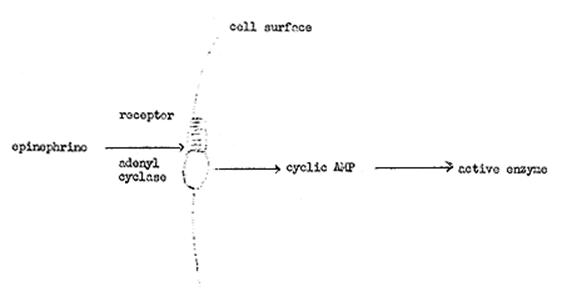
Fig 1. 薩塞蘭發現的epinephrine作用機制
 stimulate
stimulate
 Hormone
adenyl cyclase
Hormone
adenyl cyclase
 cyclic AMP
cytosolic ATP
cyclic AMP
cytosolic ATP
inactive
enzymes
active enzymes
Fig 2. 薩塞蘭提出的荷爾蒙作用機制
薩塞蘭這個新構想,能解釋許多激素的作用機制,因此在1971年榮獲諾貝爾生理醫學獎。
當薩塞蘭提出這個假設時,曾引起學界廣泛的辯論,由於許多研究者認為細胞受激素引起的各種不同反應不可能是經由同一個物質(cAMP)所引發。直到1960年代,他的假設才得到證明。他甚至還證明在細菌內也具有cAMP。後來我們發現即使在單細胞生物內,cAMP依然扮演重要角色,故有學者認為cAMP可能是最原始的hormone。如今,我們知道各種不同的激素在目標細胞(target
cells)表面有它專一的接受器(specific receptors),而引發cAMP活化不同的化學反應途徑;且即使是相同的激素,在不同的目標細胞也可能產生不同的反應。現在我們將這些細胞自接受激素起引發的一連串的反應稱為訊息傳導(signal
trasduction)。而這一切後續的研究都是奠基於薩塞蘭發現荷爾蒙的作用機制。(3,6)
參考資料
1. http://www.ntttc.edu.tw/sccenter/natural/生物學家/諾貝爾生理醫學獎得主簡介/諾貝爾生理醫學獎得主簡介表.html
2. http://www.nobel.se/medicine/laureates/1971/index.html
3. http://140.122.143.143/NSC/bionetwork/biorelative/enzyme.html
4. http://almaz.com/nobel/medicine/1971a.html
5. http://www.britannica.com/nobel/nobelprizes.html
6. Wayne M. Becker, Lewis J. Kleinsmith,
Jeff Hardin,The World of the Cell,The Benjamin/Cummings Publish Company,2000,5th
edition,267~272
附錄:薩塞蘭生平簡歷 (1)
Earl W. Sutherland, Jr. – Curriculum Vitae
Born: Burlingame,
Kansas, November 19, 1915 Married:
1963
Children: 2 sons, 2
daughters
Education:B.S. Washburn
College, 1937
M.D. Washington
University, School of Medicine 1942, St. Louis
Professional
Experience:
Interneship,
Barnes Hospital, 1942
Assistant in
Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Washington University 1940-42
Instructor in
Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Washington University 1945-46
Instructor in
Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Washington University 1946-50
Assistant
Professor of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Washington University
1950-52
Associate
Professor of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Washington University
1952-53
Professor
Pharmacology and Director of the Department, School of Medicine, Western
Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, 1953-63
Professor of
Physiology, Vanderbilt University, School of Medicine, Nashville, Tenn.,
1963- present
Career
Investigator - American Heart Association 1967
Editorial
Board:
Biochemical
Preparations, 1951-56
Journal of
Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 1957-58
Panel of
Metabolism, Section on Biochemistry of the Committee on Growth (Nat. Res.
Council) , 1953-54
Study Section
(Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics) Public Health Service, 1954-58
Member,
National Institutes of Health Pharmacology Training Committee 1958-62,
1963-65
Member,
National Institutes of Health Arthritis and Metabolic Disease Program
Committee 1966-
Dr.
Sutherland died in 1974.